- East Of Kailash, New Delhi-110065
- +91-11-26238444
- [email protected]
"TB" for Ladies
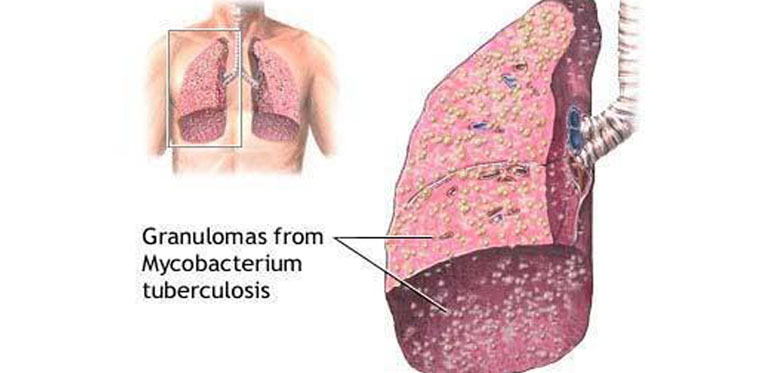
Tuberculosis (TB) is a common and often deadly infectious disease caused by mycobacterium, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis in humans. Tuberculosis usually attacks the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body. It is spread through the air, when people who have the disease cough, sneeze, or spit. Most infections in humans result in an symptomatic, latent infection, and about one in ten latent infections eventually progresses to active disease, which, if left untreated, kills more than half of its victims. The classic symptoms are a chronic cough with blood-tinged sputum, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Infection of other organs causes a wide range of symptoms. Diagnosis relies on radiology (commonly chest X-rays), a tuberculin skin test, blood tests, as well as microscopic examination and microbiological culture of bodily fluids. Treatment is difficult and requires long courses of multiple antibiotics. Contacts are also screened and treated if necessary. Antibiotic resistance is a growing problem in (extensively) multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis. Prevention relies on screening programs and vaccination, usually with Bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccine. A third of the world's populations are thought to be infected with M. tuberculosis, and new infections occur at a rate of about one per second. The proportion of people who become sick with tuberculosis each year is stable or falling worldwide but because of population growth, the absolute number of new cases is still increasing. In 2007 there were an estimated 13.7 million chronic active cases, 9.3 million new cases, and 1.8 million deaths, mostly in developing countries. The World Health Organization (W.H.O.) declared TB a global health emergency in 1993, and the Stop TB Partnership developed a Global Plan to Stop Tuberculosis that aims to save 14 million lives between 2006 and 2015. In terms of population coverage, India now has the second largest DOTS (Directly Observed Treatment, Short course) Programme in the world. However, India's DOTS Programme is the fastest expanding Programme, and the largest in the world in terms of patients initiated on treatment, placing more than 100,000 patients on treatment every month. This site provides information about tuberculosis and its control in India.
From 2007 through our awareness Programme we have work in both rural and urban area in the urban some women smoke and show their high profile and some poor women living in congested place or house mad effected with this disease and in rural due to dust and communicable it spread to others. So we request the people for proper medical treatment and use DOTS regularly. For details please read our broachers.
In terms of population coverage, India now has the second largest DOTS (Directly Observed Treatment, Short course) programme in the world. However, India's DOTS programme is the fastest expanding programme, and the largest in the world in terms of patients initiated on treatment, placing more than 100,000 patients on treatment every month. This site provides information about tuberculosis and its control in India.
HIV and TB form a lethal combination each multiplying the impact of the other in developing countries. TB is a major cause of morbidity in women in India; more women die from TB than all other causes of maternal mortality put together. TB mortality and case fatality rates of young women in reproductive age are higher than in men of same age. Issues Low birth weight, lack of education, malnutrition, early marriage and reproductive burden, gender inequality, lack of decision making rights and access to medical aid, presence of RTIs increase vulnerability of women to HIV/AIDS and TB.
Once HIV/AIDS is acquired, they become more vulnerable to the highly opportunistic infection like TB. Description The study identifies cultural, gender, socio-economic and biological determinants operating synergistically, and analyses how HIV infected women in India become vulnerable to TB. Lessons Learned Qualitative research methods such as individual interviews and limited focus group discussions are more effective in dealing with sensitive issues of sexual health and HIV/AIDS.
Generation of gender disaggregated epidemiological and social science data is essential to understand treatment-seeking and treatment default behaviour among women. Researchers and paramedics should be trained to acquire special skills for field feedback and programme implementation. Recommendations Life cycle approach has to be adopted to understand determinants of women' s health and meet their diverse health care needs. Interventions for promoting gender equality, motivation of paramedics, affordable health care services, nutritional supplement till cure, involvement of NGOs, community strategies and sensitive le gislation towards women empowerment are urgent needs.
Medical
- Asthmatic
- Medicine Distribution
- Medical Check Up
- Family Planning
- "TB" for Ladies
- Diabetes
- Women On Spines











